
In today’s digital world, various entities gather personal information for diverse purposes. This process often raises questions about transparency and consumer rights. With numerous firms vying for user data, it becomes essential to explore how these organizations manage the information they acquire. Many individuals are unaware of the extent to which their details are captured and utilized. Consequently, navigating this landscape is crucial for maintaining privacy.
One prominent player in this arena is Infogroup. Unlike typical companies, they operate within a complex framework that involves a range of practices. This intricate system plays a significant role in shaping the experience of individuals when it comes to the visibility of their personal information. As various mechanisms are employed to gather insights, understanding the implications of such operations is vital.
Moreover, users often seek a way to safeguard their personal data. The growing awareness around privacy has led many to inquire about what options are available to them. While some may feel overwhelmed by the intricacies of the process, recognizing the tools to control one’s information is a step forward. Essentially, it demands a deeper look into how entities interact with individuals in this information age.
In essence, examining the practices of this organization can illuminate critical aspects of consumer privacy. As more individuals take an interest in what happens to their personal details, the need for clarity increases. This exploration not only fosters awareness but also encourages informed decisions regarding personal information management. Ultimately, navigating the complex relationships within this environment will empower consumers to take charge of their privacy.
Understanding Infogroup’s Data Collection Practices
The methods employed to gather information are varied and multifaceted. This organization utilizes numerous techniques to compile extensive profiles on individuals and businesses. The goal is to create a comprehensive database that can be valuable for marketing and analysis purposes. Different approaches are used to ensure accuracy and relevance in the information amassed.
- Surveys are a common tool to obtain firsthand insights.
- Public records provide a wealth of information that is often overlooked.
- Purchasing information from third-party sources is another frequent approach.
- Online interactions, including social media engagements, offer a glimpse into consumer behavior.
As technology advances, innovative techniques are also being adopted. For instance, algorithms analyze user behaviors across various platforms to glean additional insights. This blend of traditional methods with cutting-edge technology enhances the depth and accuracy of the information gathered. The organization also engages in partnerships with other entities, further expanding their reach. By leveraging shared databases, a broader spectrum of data becomes accessible, which is instrumental in refining marketing strategies.
- Web scraping techniques help extract information from websites.
- Mobile applications often yield behavioral data from users.
- Customer feedback, reviews, and ratings contribute to understanding preferences.
Another aspect worth noting is the importance of consent in these practices. Although many consumers may not be fully aware, a significant amount of information is generated simply through their interactions online. This can include everything from browsing habits to purchasing patterns. Ultimately, these strategies aim to create a more personalized experience for both clients and consumers. Understanding how such information is curated is essential for grasping the broader implications of these practices.
Types of Data Collected by Infogroup
Understanding the various forms of information gathered by Infogroup provides insight into their operations. This company acquires a wide range of material, each piece serving different purposes. The expanse of information can be astonishing. From basic contact details to intricate behavioral patterns, the spectrum is broad. What is truly intriguing is how this information is categorized and utilized.
Personal details often include names, addresses, and phone numbers. This fundamental information is essential for basic identification. Additionally, demographic insights such as age, gender, and household income are frequently compiled. Such attributes help in creating profiles tailored to specific target audiences.
Beyond the essentials, a variety of behavioral attributes are obtained. These include purchasing habits, interests, https://migration-bt4.co.uk/profile.php?id=613497 and lifestyle choices. Companies often rely on this information to understand consumer preferences. It’s crucial for them to engage effectively with potential clients. Moreover, geographical data helps in mapping consumer behaviors across different regions.
To illustrate the range of information collected, the following table summarizes key types:
Type of Information
Description
Contact Information
Names, addresses, phone numbers.
Demographics
Age, gender, household income.
Behavioral Data
Purchasing habits, interests, lifestyle choices.
Geolocation
Consumer behaviors mapped by region.
Understanding the methods of information gathering reveals significant implications. This variety not only enhances marketing strategies but also shapes consumer experiences. The interconnectedness of such data creates a nuanced understanding of consumer behavior. It underscores the importance of transparency in these processes, as individuals increasingly seek control over their personal information.
How Infogroup Utilizes Collected Information

Understanding how information is utilized reveals much about the underlying motives. Companies often seek to maximize the value of the insights they gather. They create strategies that cater to various sectors and needs. This can lead to improved targeting and customer engagement. The ways in which this information is employed can be quite diverse.
One significant aspect is the focus on marketing efforts. By analyzing consumer behavior and preferences, organizations can craft tailored campaigns. This allows them to reach specific audiences effectively. Potential customers receive offers that resonate with their interests, improving conversion rates. Furthermore, businesses can adapt their products or services based on the insights gained.
- Market research enhancement
- Business intelligence for strategic decisions
- Customer segmentation and personalized marketing
- Risk assessment and fraud prevention
Moreover, insights are invaluable for operational efficiency. Companies can streamline processes, identify areas for improvement, and allocate resources more effectively. When organizations understand their clients better, they can anticipate needs and respond to changes in the market swiftly. This adaptability is crucial in today’s fast-paced environment.
Additionally, customer profiles generated from the gathered insights help in developing new products. Companies often assess demographic data to identify gaps in the market. As a result, they can create innovative solutions that cater specifically to unmet demands. In doing so, they not only enhance their offerings but also foster customer loyalty through responsiveness.
Lastly, it’s noteworthy that the information is also shared with third parties. This practice enables a wider network of businesses to benefit from the insights. Partners may include advertisers, retailers, or even research institutions that seek to understand broader market trends. Such collaborations can amplify the reach and effectiveness of marketing strategies, illustrating just how interconnected this ecosystem is.
Opt-Out Process for Consumers
In today’s digital age, individuals often find themselves unwittingly part of extensive information networks. Many companies compile vast amounts of personal information, which can sometimes feel intrusive. While this practice supports targeted marketing and personalized services, it raises significant privacy concerns. As a result, there are options available for those wishing to regain control over their personal details. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for anyone concerned about their online footprint.
The process for consumers to remove or limit the use of their information varies by organization. Here’s a closer look at the steps involved:
- Identify the entity you’re dealing with.
- Visit the official website for specific instructions.
- Prepare any necessary personal information required for verification.
- Complete the opt-out form as instructed.
- Confirm the completion of the opt-out process through email or notifications.
It is important to note that despite the straightforward nature of these steps, many individuals may encounter challenges along the way, such as understanding the requirements or facing technical issues. Furthermore, some entities may require periodic renewals or confirmations to maintain your request, complicating an already intricate process.
In addition to these practical steps, consumers should educate themselves about their rights concerning personal information. Awareness is a powerful tool–knowledge can empower individuals to act decisively when they feel their privacy is at stake. Ultimately, while each company has its specific guidelines, the core principle remains the same: consumers should have the right to make informed choices about their personal information.
Moreover, it is essential to recognize that opting out doesn’t mean complete anonymity. Some information may still remain accessible through other channels or systems. Thus, consumers should regularly review their online presence to ensure it aligns with their privacy preferences. Regular audits of personal information can lead to better control over one’s digital identity.
In conclusion, navigating the terrain of personal information management requires diligence and proactivity. By understanding the opt-out processes and exercising their rights, individuals can take significant steps toward safeguarding their privacy in an increasingly interconnected world.
Implications of Data Broker Operations
The operations of information brokers have far-reaching consequences for various stakeholders. Consumers often remain unaware of how their personal details are utilized. This lack of transparency can lead to significant privacy concerns. Moreover, businesses rely heavily on the insights provided by these entities. The implications ripple through society, affecting how individuals interact with brands and services.
For many, the realization that personal information is sold and shared can be unsettling. It raises questions about trust and integrity. When a company accesses sensitive data, it inherently shifts the power dynamic between the consumer and the organization. The average person may struggle to comprehend the scope of data exchange in today’s digital landscape.
Furthermore, businesses face both opportunities and challenges arising from this information exchange. Enhanced targeting capabilities can drive efficient marketing strategies. However, the ethical implications of using personal details complicate the narrative. Companies must navigate the fine line between effective marketing and invasive practices.
Legally, the landscape surrounding information utilization is evolving. Regulations are being introduced to protect consumer rights, but enforcement remains inconsistent. This inconsistency creates a challenging environment for all parties involved. As awareness of privacy issues grows, stakeholders must adapt to new expectations.
In summary, the operations of information brokers influence many aspects of consumer-business relationships. They shape marketing strategies, impact privacy perceptions, and challenge legislative frameworks. Understanding these implications is crucial for navigating the modern economy. With innovation comes responsibility, and all players must recognize their roles in this dynamic ecosystem.
Comparing Infogroup with Other Data Brokers
In the realm of information providers, various entities operate under differing principles and methodologies. Each organization has its own strengths, weaknesses, and unique approaches to gathering insights. This diversity can significantly influence how personal information is handled. Consumers must navigate through this complex landscape carefully. Understanding the dynamics between different suppliers is crucial.
Examining Infogroup alongside its competitors reveals fascinating contrasts. For instance, while some enterprises focus primarily on commercial data, others may delve into public records or demographic insights. Infogroup strategically targets businesses, aiming to enhance their marketing efforts through refined customer profiling. However, others might prioritize aggregating personal experiences or online behaviors to create a holistic view.
Moreover, the methodologies employed by these entities vary widely. Some rely heavily on technology to scrape data from various sources, whereas others invest more heavily in traditional surveying methods. This difference in approach can lead to variations in accuracy and depth. In many cases, the techniques used significantly impact the quality of information provided.
It is also vital to consider the ethical dimensions associated with these operations. Different organizations embrace varying degrees of transparency in their practices. Some are committed to ensuring user privacy and openly communicate their policies, while others tend to operate with less accountability. This divergence raises important questions about consumer trust and industry standards.
Furthermore, the legal frameworks surrounding these entities can dictate their operational capacities. With evolving regulations, some suppliers adjust their tactics to remain compliant, while others may face penalties for non-adherence. The implications of these regulations foster a climate of competition and innovation, compelling organizations to enhance their offerings continually.
In conclusion, as consumers become increasingly aware of their information’s journey, the differences between various purveyors of insights will likely play a pivotal role in shaping industry trends. An informed consumer is an empowered one, able to make choices that align with their values and expectations regarding privacy and ethical practices.
Consumer Rights and Data Privacy
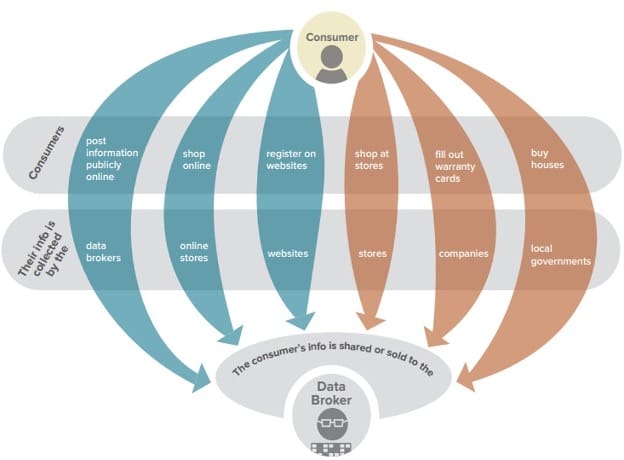
In today’s digital world, ensuring the protection of personal information has become increasingly important. Consumers are often unaware of the extent to which their private details are shared or sold. The complexities surrounding privacy rights can lead to confusion. Therefore, it’s crucial to understand the rights that individuals possess.
There are several key components regarding consumer rights:
- Right to Access
- Right to Rectification
- Right to Erasure
- Right to Data Portability
- Right to Object
The right to access allows individuals to request information about what personal details are held by various entities. This fosters transparency and empowers consumers to make informed choices about their information. Additionally, people can ask for inaccuracies to be corrected, ensuring that their records remain accurate. The right to erasure, often referred to as the ‘right to be forgotten,’ gives consumers the ability to request deletion of their data under certain conditions.
Moreover, individuals can demand that their information be transferred to another service, reinforcing the importance of maintaining control over personal information. Consumers also possess the right to object to specific uses of their data, providing a layer of protection against unwanted sharing.
With the rise of stringent regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, stronger safeguards are being implemented. These laws establish comprehensive frameworks for protecting individual privacy and hold organizations accountable for mishandling personal information. As a result, businesses must adopt more transparent practices, ensuring that consumers are aware of how their information is utilized.
In the United States, the legal landscape surrounding privacy rights is more fragmented. Various states have introduced their own regulations, leading to a patchwork of laws. This inconsistency can pose challenges for consumers who may struggle to understand their rights across different jurisdictions. A growing demand for a cohesive federal approach to privacy protection has emerged, highlighting the need for updated legislation.
As the landscape continues to evolve, individuals must remain vigilant. Staying informed about changes in privacy laws is essential in exercising one’s rights effectively. Additionally, organizations should prioritize consumer education regarding privacy options and empower individuals to take control of their information.
Ultimately, the conversation surrounding consumer rights and privacy is ongoing. As technology continues to develop, so too will the expectations for transparency and accountability. A collective effort between consumers, policymakers, and businesses is crucial in fostering a safer digital environment.
Consumer Rights and Data Privacy
In today’s digital landscape, understanding individual rights concerning personal information is essential. The growing reliance on technology has resulted in a significant shift in how private details are handled. Consumers often feel overwhelmed by the complex web of regulations and practices surrounding their information. Empowering individuals with knowledge is crucial. Awareness leads to better decision-making.
Consumers have a fundamental right to control their personal information. This right encompasses knowledge of how details are used, who accesses them, and the ability to withdraw consent when desired. Furthermore, it’s vital to ensure that individuals are educated about potential risks associated with indiscriminate sharing.
- Right to Know: Consumers should have access to information about their data’s usage.
- Right to Access: Individuals can request copies of the information held about them.
- Right to Rectification: Consumers can correct inaccurate or incomplete data.
- Right to Erasure: There is a possibility to demand the deletion of personal details.
- Right to Object: Individuals may resist the processing of their details under certain circumstances.
As laws evolve, many countries are adopting more stringent regulations aimed at protecting personal information; this shift underscores the importance of consumer empowerment and transparency. In the United States, for example, several states have introduced privacy laws that give individuals more control over their information. The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is one such law that has set a precedent. It grants consumers rights that include the ability to know what data is being collected about them and to whom it is being sold. Similarly, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe has implemented robust measures to safeguard personal information. These regulations are shaping a new era in which consumers are expected to play a more active role in managing their information.
Protecting personal information is not just beneficial for consumers; it also fosters trust between individuals and organizations. When people feel confident that their details are safeguarded, they are more inclined to engage with various services. Conversely, a lack of transparency can lead to significant backlash and loss of reputation for companies. This dynamic relationship between consumers and organizations emphasizes the pivotal role of data privacy in modern society.
In conclusion, the significance of understanding personal rights related to privacy cannot be overstated. As consumers become more informed and vigilant, they can navigate the complexities of today’s digital environment more effectively. Staying aware of one’s rights is the first step toward safeguarding personal information in an increasingly interconnected world.
Future Trends in Data Brokerage
The landscape of information trade is shifting rapidly. As technology evolves, so do the methods and practices of firms engaged in this sector. New challenges are emerging, shaped by advancements in artificial intelligence, privacy regulations, and consumer awareness. Increased scrutiny from both the public and lawmakers is creating a dynamic environment.
One key trend is the growing importance of transparency. Consumers are becoming more discerning about how their personal information is handled. They demand clarity about where their information goes and how it is used. This shift is prompting companies to adopt clearer practices.
Additionally, the advent of stricter legislation is reshaping operations. Governments across the globe are implementing regulations aimed at protecting consumer rights. Initiatives such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe have set a precedent for stringent compliance standards. As a result, organizations must reassess their methodologies to align with evolving legal frameworks.
Another noteworthy development is the rise of ethical data use. Businesses are recognizing the importance of cultivating trust with their clientele. Ethical considerations are no longer merely optional; they are becoming integral to successful operations. Companies that prioritize responsible practices may find themselves at a competitive advantage.
Moreover, advancements in technology are enabling more sophisticated analytical techniques. Companies are harnessing machine learning and big data analytics to derive insights from vast amounts of information. This capability allows for enhanced targeting and personalization, significantly improving the effectiveness of marketing strategies. However, it also raises questions about potential misuse and ethical implications.
The integration of blockchain technology represents yet another promising trend. By providing a decentralized approach, this technology offers the potential for greater security and transparency in transactions involving personal information. It could empower consumers by giving them more control over their own data, ultimately leading to a more responsible environment.
In conclusion, the future of the information trade is marked by a complex interplay of transparency, ethical considerations, regulatory frameworks, and technological innovations. These elements will continue to shape the way businesses operate in this ever-evolving landscape.

